The arch is made up of many ashlars, each of which is subject to compression, which are supported by mutual contrast thanks to the piers at either end that form the vertical elements of the arch (for more information go here). The main elements of an arch are:
- ashlars, main elements of the arch that support the compressive stresses;
- keystone ashlar, is a ashlar positioned on the central top of the arch;
- intrados, the inner boundary line of the arch;
- extrados, the outer boundary line of the arch;
- piers, also called abutments, are vertical elements that support the forces transmitted by the arch;
- impost plane, is the upper end of the abutment and is the bearing plane of the first ashlar of the arch;
- radius of the arch, is the radius of the circle passing through the intrados of the arch;
- light (l) or string, is the distance between the keystone and the light (or string);
- arrow (f) or mount, is the distance between the bowstring and the keystone;
- bow kidneys, are the sections inclined 30° to the horizontal plane of the bow;
- chain, is an optional element that facilitates increasing the stability of the bow by counteracting the horizontal forces to which the abutments are subjected.

SHAPES OF THE ARCHES
The shape of the arch depends above all on its sixth. The sixth is the ratio between the arrow and half the span: f/(l/2).
There are three main types of arch:
- drop arch, when the value of the sixth is less than 1;
- semi-circular arch, if the value of the sixth is equal to 1;
- pointed arch, if the value of the sixth is greater than 1.
The shape of the bow depends above all on its sixth. The sixth is the ratio between the arrow and half the span: f/(l/2).
There are three main types of arch
- low sixth, when the value of the sixth is less than 1;
- rounded, if the value of the sixth is equal to 1;
- pointed, if the value of the sixth is greater than 1.

CONSTRUCTION OF ARCHS
The construction of arches is a very complicated process and requires first-class, highly skilled labour.
FORMATION OF THE RIB
The rib is a temporary wooden structure whose function is to support the ashlars that will form the arch and to shape the arch soffit. If the span is not large, it may present a simple structure, on the contrary it will be more complex.
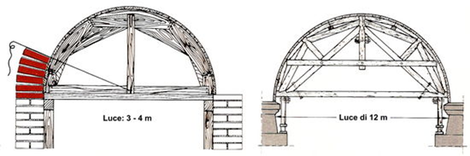
LAYING OF ASHLARS
The laying of the ashlars involves starting from the impost level and concluding with the final laying of the central key ashlar. Usually the ashlars are made of stone or brick, and for each of the two there is a different joint. In the case of stone, it is necessary to cut each ashlar in such a way that the lateral faces perfectly match those of the adjacent ashlars. In the case of bricks, on the other hand, ashlars of varying thickness are laid between the soffit and extrados profiles.

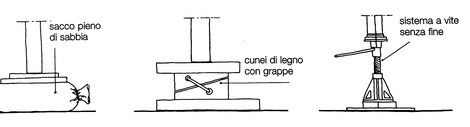
DISARMING OF THE RIBS
The stripping of the ribs is a very delicate and important phase in the formation of an arch. In fact, all of the arch elements settle under load very slowly and gradually during the dismantling process, so there must be no vibrations that lead to unbalanced stresses. There are numerous methods of dismantling, such as sandbags that are gradually emptied, wooden wedges and the worm gear system.
JACK ARCH
This is a type of arch with a straight floor intrados. Statically, it is entirely similar to the arch, with the difference being the ashlars and their installation. The laying involves the creation of an inclined impost plane (usually 60 degrees and arranged diagonally) and the laying of the inclined ashlars up to the vertical central part.
The plinth replaces the lintel placed at the crown of the openings to support the overlying part of the masonry. It was usually surmounted by a drainage arch called sordino, which had the task of reducing stresses.
Other articles:
How to insert an html code for hit counter, or view counter, into your website for free
Hydraulic and hydrogeological invariance - rainwater
collection
Index a site or page on Google with Google Search Console
how could we produce energy from the garbage we generally produce
Load-bearing brick walls and load-bearing concrete walls - What are they
The most famous women in medicine
Painting or spray painting - Advantages and disadvantages
Concrete casting carried out at low temperatures
Concrete block masonry - Installation with mortar, for gluing, corners, jambs and architrave
Ordinary continuous direct foundations, inverted beams and slab foundations
galvanic currents and stray currents what they are and how toprevent


Scrivi commento